Anatomy for artists is the study of the human body’s structure‚ essential for creating realistic and accurate depictions. It helps artists understand proportions‚ movement‚ and form‚ enabling them to capture the body’s complexity in their work. By mastering anatomy‚ artists can convey emotion‚ posture‚ and dynamic poses effectively‚ making it a cornerstone of artistic training and practice.
Definition and Importance of Anatomy in Art
Anatomy for artists is the study of the human body’s structure‚ focusing on its form‚ proportions‚ and movement. It is essential for creating realistic and expressive depictions of the body in art. Understanding anatomy allows artists to accurately capture the relationships between bones‚ muscles‚ and surface features‚ enabling them to convey emotion‚ posture‚ and dynamic poses. This knowledge is fundamental for mastering figure drawing‚ sculpture‚ and other art forms‚ making it a cornerstone of artistic training and practice.
Historical Significance of Anatomy in Artistic Training
The study of anatomy has been a cornerstone of artistic training for centuries‚ particularly during the Renaissance. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo meticulously studied the human body to create lifelike and dynamic works. Understanding anatomy allowed them to depict realistic proportions‚ movement‚ and emotion. This tradition continues today‚ as artists rely on anatomical knowledge to accurately render the human form. Historical anatomical studies remain a foundation for artistic mastery‚ bridging science and creativity to capture the essence of the human body in art.

Understanding the Human Body Structure
Understanding the human body structure involves studying the skeletal and muscular systems‚ as well as surface anatomy‚ to accurately depict proportions‚ movement‚ and form in artistic creations.
Overview of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system forms the structural framework of the human body‚ comprising 206 bones that provide support‚ protection‚ and movement. It includes the axial skeleton (skull‚ spine‚ ribcage) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs and pelvis). Joints connect bones‚ enabling flexibility and mobility. Understanding the skeletal system is crucial for artists to accurately depict proportions‚ posture‚ and movement. Bones vary in shape and function‚ from the cranium’s protective role to the phalanges’ role in finger movement. This foundation helps artists create realistic and anatomically correct figures in their work.
Muscular System and Its Role in Movement
The muscular system consists of over 600 muscles that enable movement‚ maintain posture‚ and regulate body functions. Muscles work in pairs to flex and extend joints‚ with each muscle’s shape and size influencing movement dynamics. For artists‚ understanding muscle anatomy is key to depicting realistic poses and gestures. Muscles like the deltoids‚ biceps‚ and triceps are crucial for arm movements‚ while core muscles stabilize the body. Studying how muscles interact with bones and change shape during motion helps artists create lifelike and dynamic figures in their work.
Surface Anatomy and Its Relevance to Artists
Surface anatomy refers to the study of the body’s external structures as they appear under the skin. It helps artists accurately depict the visible forms and contours created by muscles‚ bones‚ and tissues. Understanding surface anatomy allows artists to capture the subtleties of the human form‚ such as the shape of the deltoids‚ the definition of the triceps‚ and the flow of tendons. This knowledge is essential for creating realistic and dynamic figures‚ as it bridges the gap between internal anatomy and its visible expression in various poses and movements.
Proportion and Measurement in Artistic Anatomy
Proportion and measurement are crucial for accurate depictions of the human body. Artists use proportional guidelines to ensure balance and harmony in their work‚ adhering to classical standards.
Classical Proportions of the Human Body
Classical proportions provide a foundational framework for depicting the human body accurately. The body is often measured in “heads‚” with the average adult height equaling eight head lengths. This system ensures harmony and balance in artistic representations. The golden ratio and symmetrical divisions of the body are key principles‚ guiding artists to create aesthetically pleasing and anatomically consistent forms. Understanding these proportions allows artists to capture the body’s natural balance and create realistic‚ visually appealing depictions in their work.
Understanding Body Ratios and Symmetry
Body ratios and symmetry are crucial for accurate artistic depictions. The human body follows specific proportional relationships‚ such as the 1:1.618 golden ratio‚ ensuring balance and harmony. Symmetry divides the body into mirror halves‚ aiding in realistic representations. Artists use these principles to maintain consistency in poses and forms‚ ensuring anatomical accuracy. Understanding body ratios and symmetry enhances the ability to draw the body correctly‚ whether in motion or at rest‚ and is essential for creating visually appealing and realistic art.

The Upper Body: Bones and Muscles
The upper body includes the shoulder‚ chest‚ and arm structures‚ with muscles like the deltoids‚ biceps‚ and triceps enabling movement and form‚ essential for artistic accuracy.
Structure of the Shoulder and Chest
The shoulder and chest form a complex framework of bones and muscles essential for movement and stability. The scapula‚ clavicle‚ sternum‚ and ribs create the structural base‚ while muscles like the pectoralis major‚ deltoids‚ and triceps attach to these bones‚ enabling dynamic poses. Understanding the connections‚ such as the scapula’s role in shoulder movement‚ is crucial for artists to depict realistic anatomy. The chest muscles‚ including the pectoralis‚ define the torso’s shape‚ while the ribcage influences posture and breathing‚ making this area vital for accurate artistic representation.
Deltoids‚ Biceps‚ and Triceps: Key Muscles for Artists
The deltoids‚ biceps‚ and triceps are essential for understanding arm anatomy. The deltoids‚ forming the shoulder’s rounded shape‚ connect to the scapula and clavicle‚ enabling abduction and flexion. Biceps‚ located on the upper arm‚ facilitate elbow flexion and forearm supination‚ while triceps extend the elbow‚ straightening the arm. Accurately depicting these muscles requires studying their attachments and how they change shape during movement. Observing their dynamics‚ such as how the biceps bulge during flexion‚ helps artists capture realistic poses and forms in their work.

The Lower Body: Pelvis‚ Thighs‚ and Legs
The pelvis forms the foundation of the lower body‚ supporting posture and balance. Thigh muscles‚ including quadriceps and hamstrings‚ enable movement‚ while leg anatomy details calf and shin structures.
Pelvic Structure and Its Importance in Posture
The pelvis is a complex bony structure forming the base of the spine and lower limb system. It consists of the ilium‚ ischium‚ and pubis bones‚ which fuse at the acetabulum to form the hip socket. The sacrum‚ connected to the spine‚ articulates with the ilium‚ creating the sacroiliac joint. This structure supports the body’s weight and facilitates balance. Understanding pelvic anatomy is crucial for artists‚ as it influences posture‚ movement‚ and the overall proportions of the figure. Accurate depiction of the pelvis enhances the realism and authenticity of artistic representations of the human form.
Thigh and Calf Muscles: Anatomy for Realistic Depiction
The thigh muscles‚ including the quadriceps‚ hamstrings‚ and adductors‚ play a crucial role in movement and posture. The quadriceps extend the knee‚ while the hamstrings flex it. The adductors stabilize the thigh. In the lower leg‚ the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles form the calf‚ essential for foot flexion. Accurate depiction of these muscles requires understanding their attachments and how they influence the body’s outline. Artists should study their dynamic shapes and functions to capture realistic movement and form in their work‚ ensuring anatomical accuracy and visual appeal.

The Head and Hands: Detailed Anatomy
Mastering the intricate anatomy of the head and hands is vital for artists. Understanding bone structure‚ muscle placement‚ and facial expressions ensures realistic and detailed depictions in artwork.
Skull Structure and Facial Anatomy
The skull forms the foundation of the head‚ comprising the cranium and facial bones. Understanding its structure‚ including the orbits‚ nasal cavity‚ and jaw alignment‚ is crucial for accurate depictions. Facial anatomy involves muscles like the zygomaticus and orbicularis oculi‚ which control expressions. Artists must study how bones and muscles interact to create realistic facial features and emotions. Detailed knowledge of these elements enhances the ability to draw lifelike portraits and capture subtle expressions effectively in artwork.
Hand and Finger Anatomy: Complexity and Detail
The human hand is a masterpiece of anatomy‚ with 27 bones‚ 29 joints‚ and over 120 muscles. Each finger contains three phalanges‚ except the thumb‚ which has two; The wrist comprises eight carpal bones‚ while the metacarpals connect the hand to the forearm. Artists must study the intricate relationships between these bones‚ tendons‚ and ligaments to capture the hand’s flexibility and precision. Understanding the hand’s structure allows for realistic depictions of gestures‚ grip‚ and expression‚ making it a vital focus for artistic accuracy and detail.
Equilibrium and Locomotion
Equilibrium and locomotion are vital for understanding human movement and balance. Artists study how the body maintains stability and transitions between poses‚ ensuring dynamic and realistic depictions in art.
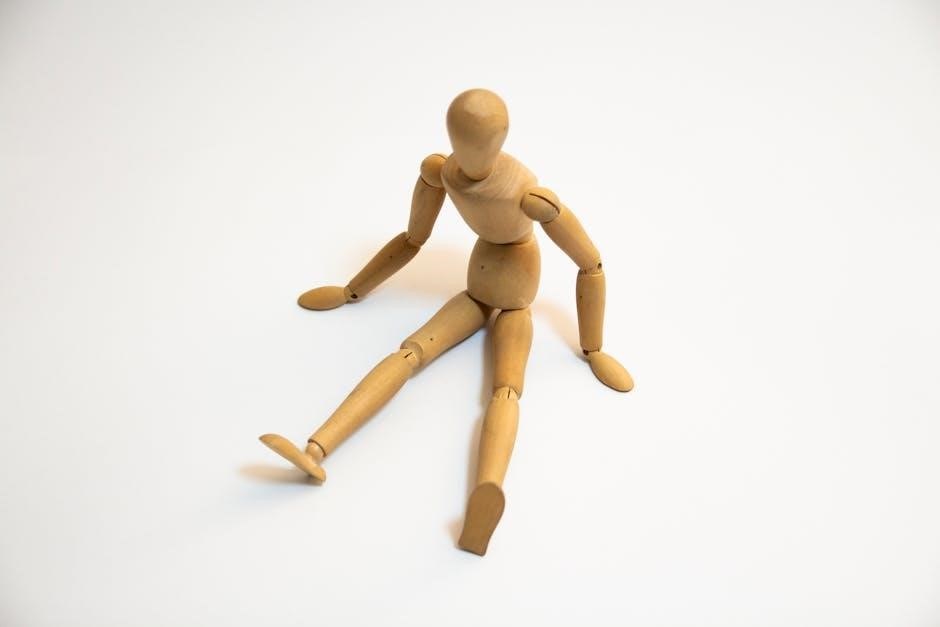

Balance and Weight Distribution in Art
Balance and weight distribution are crucial for creating realistic and dynamic poses in art. Understanding how the body maintains equilibrium helps artists depict natural postures and movements. The center of gravity plays a key role‚ influencing how weight shifts between limbs and torso. Accurate representation of these principles ensures compositions feel stable and lifelike. Artists study how muscles and bones interact to achieve balance‚ enabling them to capture the subtleties of human movement and posture in their work effectively.
Understanding Movement and Gesture Drawing
Gesture drawing captures the essence of movement and energy in the human body. It involves quick sketches to convey posture‚ balance‚ and fluidity. Artists study how muscles and bones interact during motion‚ allowing them to depict dynamic poses accurately. This practice enhances the ability to render lifelike movement and expression. By observing how weight shifts and limbs extend‚ artists can create compositions that feel natural and full of energy. Gesture drawing is a foundational skill for mastering anatomy and bringing vitality to artistic depictions of the human form.

Age‚ Sex‚ and Race: Anatomical Distinctions

Anatomy varies across age‚ sex‚ and race‚ influencing body proportions‚ muscle structure‚ and facial features. These distinctions help artists create diverse‚ realistic‚ and culturally accurate depictions of the human form.
Anatomical Differences Across Age Groups
Anatomy varies significantly across age groups‚ influencing body proportions‚ muscle definition‚ and posture. Children have softer‚ rounder features with developing bones‚ while adults exhibit fully formed structures. Elderly individuals often show bone density loss‚ muscle atrophy‚ and altered postures. Understanding these changes enables artists to accurately depict characters of different ages‚ capturing the unique qualities of each life stage. This knowledge enhances realism and emotional depth in artwork‚ making it essential for creating authentic and relatable human forms.
Sexual Dimorphism in Human Anatomy
Sexual dimorphism in anatomy refers to the physical differences between males and females. These distinctions include skeletal structure‚ muscle mass‚ and body composition. Male bodies often exhibit broader shoulders‚ a more pronounced jawline‚ and greater upper body strength‚ while female bodies typically have a wider pelvis‚ narrower shoulders‚ and a higher proportion of body fat. Understanding these differences is crucial for artists to accurately depict gender-specific features‚ ensuring realistic and nuanced representations of male and female forms in their work.
Racial Variations in Anatomical Structure
Racial variations in anatomy involve differences in physical traits among diverse populations. These include facial features‚ body proportions‚ and bone structure. For example‚ facial anatomy varies in contour‚ while limb proportions and muscle attachments differ slightly. Understanding these variations helps artists create authentic and culturally sensitive depictions. By studying racial anatomical differences‚ artists can accurately represent diverse subjects‚ ensuring their work reflects the richness of human diversity while maintaining anatomical accuracy and respect for individual and cultural uniqueness.
Agents of Expression: Anatomy in Emotion
Anatomy plays a crucial role in conveying emotion through facial expressions and body language. Muscles‚ particularly around the face and eyes‚ reveal feelings‚ while posture reflects mood and intent.
Facial Expressions and Muscle Movements
Facial expressions are driven by the subtle movements of muscles beneath the skin. Artists must understand how these muscles contract and relax to create emotions. The zygomaticus major lifts the cheeks for a smile‚ while the corrugators furrow the brow in concern. Observing these details helps capture authenticity. Using anatomical references and 3D models can enhance accuracy. Practicing gesture drawing and studying real-life expressions are essential for mastering emotional portrayal in art. This knowledge allows artists to convey complex feelings through precise anatomical rendering.
Body Language and Posture in Art
Body language and posture are vital for conveying emotion and narrative in art. Understanding anatomy helps artists accurately depict how the body communicates through stance and movement. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to create dynamic poses‚ from the subtle curvature of the spine to the tension in the limbs. Studying how muscles like the trapezius and erector spinae influence posture can enhance realism. Observing life models and using anatomical references‚ such as 3D models‚ allow artists to capture the essence of body language effectively in their work.

Recommended Resources for Artists
Essential resources include anatomy books like Anatomy for the Artist by Sarah Simblet and Figure Drawing: Design and Invention by Michael Hampton. Utilize online tools like Croquis Cafe and 3D anatomy apps for interactive learning.
Best Anatomy Books for Artists
Top anatomy books for artists include Anatomy for the Artist by Sarah Simblet‚ offering detailed drawings and photos‚ and Figure Drawing: Design and Invention by Michael Hampton‚ which simplifies complex forms. Anatomy for Sculptors is also highly recommended‚ providing insights into 3D structure. These books‚ along with Die Gestalt des Menschen by Gottfried Bammes‚ offer comprehensive guides for understanding human anatomy. They are invaluable for mastering proportions‚ muscle structure‚ and realistic depictions‚ making them essential tools for both beginners and advanced artists.
Online Courses and Tutorials for Anatomy Study
Online platforms like Croquis Cafe on Vimeo and Proko offer exceptional resources for anatomy study. Proko‚ by Stan Prokopenko‚ provides detailed video lessons on anatomy and figure drawing. New Masters Academy features expert-led courses on human anatomy‚ while Anatomy 360 offers 3D models and tutorials. These resources allow artists to learn from professionals‚ practice gesture drawing‚ and explore interactive tools. They are ideal for both beginners and advanced artists seeking to refine their understanding of human anatomy and improve their artistic skills.
3D Models and Apps for Interactive Learning
3D anatomy apps like Anatomy 3D Atlas and Complete Anatomy offer interactive models for artists to explore the human body in depth. These tools provide detailed views of muscles‚ bones‚ and organs from multiple angles‚ enhancing understanding of structure and movement. Features like quizzes and layered dissection simulate real anatomical study‚ making them ideal for both traditional and digital artists. Apps such as Anatomy.app also include interactive lessons and 3D simulations‚ allowing artists to engage with anatomy in a dynamic and immersive way‚ perfect for refining their artistic skills.
Practical Exercises for Mastering Anatomy
Practice gesture drawing‚ quick sketches‚ and long-pose studies to refine your understanding of anatomy. These exercises help capture movement‚ proportions‚ and details‚ enhancing your artistic accuracy and skill.
Gesture Drawing and Quick Sketches
Gesture drawing and quick sketches are essential exercises for capturing the fluidity and movement of the human body. These practices help artists develop an understanding of form‚ proportion‚ and structure. By focusing on rapid‚ expressive drawings‚ artists can improve their ability to convey dynamic poses and anatomical accuracy. Start with short gestures (1-5 minutes) to loosen up and capture the essence of movement. Gradually incorporate longer studies to refine details. These exercises enhance observational skills and muscle memory‚ making them indispensable for mastering anatomy in art.
Long-Pose Drawings for Detail and Accuracy
Long-pose drawings allow artists to delve into intricate anatomical details‚ ensuring precision and accuracy. These extended sessions enable a thorough study of bone structures‚ muscle definitions‚ and surface anatomy. By focusing on a static pose‚ artists can refine their understanding of proportions‚ contours‚ and the interplay of light and shadow. This practice fosters patience and attention to detail‚ helping to develop a deeper connection with the subject. Long-pose drawings are crucial for mastering the subtleties of human anatomy and translating them into realistic‚ visually compelling artwork.
Short Studies of Individual Body Parts
Short studies of individual body parts are essential for mastering anatomy. By focusing on specific areas like hands‚ feet‚ or facial features‚ artists can achieve precise detail and accuracy. These exercises help in understanding the structure‚ proportions‚ and functionality of each part. Regular practice allows artists to develop muscle memory and improve their ability to depict complex forms. Breaking the body into manageable sections ensures a deeper understanding‚ which ultimately enhances the overall quality of artistic compositions and realistic depictions.
Modern Tools for Anatomy Study
Modern tools for anatomy study include 3D software‚ apps‚ and VR‚ offering interactive models and real-time visualization to enhance artistic understanding of the human body.
3D Anatomy Software and Apps
3D anatomy software and apps provide interactive models of the human body‚ allowing artists to explore muscles‚ bones‚ and organs in detail. These tools enable precise study of anatomical structures from multiple angles‚ enhancing understanding of form and movement. Apps like Anatomy 3D Atlas and Anatomy.app offer layered models‚ quizzes‚ and tutorials‚ making them invaluable for both 2D and 3D artists. They simplify complex anatomy‚ aiding in realistic depictions and helping artists master proportions and muscle dynamics effectively.
Interactive Websites for Anatomical Exploration
Interactive websites like Kenhub and Visible Body offer detailed 3D models and quizzes‚ enabling artists to explore anatomy dynamically. These platforms provide layered views of muscles‚ bones‚ and organs‚ allowing for a deeper understanding of the body’s structure. Artists can rotate models‚ isolate specific parts‚ and study anatomical relationships‚ making these tools invaluable for mastering proportions and movement. Such resources bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application‚ enhancing the accuracy and realism in artistic depictions of the human form.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Anatomy Education
Virtual Reality (VR) revolutionizes anatomy education by offering immersive‚ 3D explorations of the human body. Artists can examine intricate structures‚ such as muscles and bones‚ from any angle‚ enhancing their understanding of form and movement. VR platforms provide interactive tools‚ allowing users to zoom‚ rotate‚ and label anatomical features. This technology enables artists to visualize complex relationships between body parts‚ aiding in the creation of more accurate and dynamic depictions. VR anatomy education is a powerful tool for mastering human anatomy‚ making it an invaluable resource for artistic training and practice.
Community and Continuous Learning
Joining art communities provides valuable feedback and growth opportunities. Engaging in workshops and continuous practice fosters mastery of anatomy‚ essential for artistic development and realistic depictions.
Joining Art Communities for Feedback and Growth
Engaging with art communities like Croquis Cafe on Vimeo offers invaluable feedback and growth opportunities. These platforms connect artists globally‚ fostering learning through shared resources and critiques. Participating in workshops and classes enhances anatomical accuracy and artistic expression. Interactive tools like 3D anatomy apps and online tutorials supplement community learning‚ providing dynamic ways to study and refine skills. Collaborative environments encourage continuous improvement‚ helping artists master anatomy and achieve realistic‚ expressive depictions in their work.
Workshops and Classes for Anatomy Mastery
Workshops and classes are essential for refining anatomical knowledge and artistic skills. Programs like those offered by lifedrawing.academy provide structured learning‚ combining theory with practical exercises. Books such as Anatomy for the Artist by Sarah Simblet and Figure Drawing: Design and Invention by Michael Hampton are often used in these courses. Interactive tools and live model sessions enhance understanding‚ while expert feedback helps correct mistakes. These resources and structured learning paths are vital for mastering anatomy and achieving artistic excellence in drawing the human form accurately and expressively.



